 | Types of Chemical Reactions
Examples of
Multiple Choice Questions
|
- 1.
- What alkaline earth metal is located in period 3?
- (a) Li
- (b) Na
- (c) Ca
- (d) Mg
- (e) Sr
- 2.
- Which of the following is classified as a metal?
- (a) Ge
- (b) As
- (c) F
- (d) V
- (e) Ar
- 3.
- Which of the following is a weak acid?
- (a) H2SO4
- (b) HClO3
- (c) HF
- (d) HCl
- (e) HNO3
- 4.
- Which one of the following is likely to be the most soluble base?
- (a) Ca(OH)2
- (b) Cu(OH)2
- (c) Ga(OH)3
- (d) Zn(OH)2
- (e) Zr(OH)3
- 5.
- Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- (a) One mole of any acid will ionize completely in aqueous solution to produce one mole of H+ ions.
- (b) Solutions of weak acids always have lower concentrations of H+ than solutions of strong acids.
- (c) There are several common acids that are insoluble.
- (d) All of the IA and IIA metal hydroxides are soluble.
- (e) All weak acids are insoluble.
- 6.
- Consider the following reaction:
NH3(g) + H2O(l) 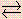 NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
Which one of the following statements is false?
NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
Which one of the following statements is false?
- (a) The double arrows indicate that ammonia, NH3, is only very slightly soluble in water.
- (b) The reaction is reversible.
- (c) When ammonia is added to water, NH4+ and OH- ions are produced in a 1:1 ratio.
- (d) When solutions of NH4Cl and NaOH are mixed, some ammonia is produced.
- (e) Ammonia is considered to be a weak base.
- 7.
- Which one of the following salts is insoluble?
- (a) NH4Cl
- (b) Ca(NO3)2
- (c) BaCO3
- (d) Na2S
- (e) Zn(CH3COO)2
- 8.
- What salt is formed in the following acid/base reaction?
HClO3 + Ba(OH)2 
- (a) BaCl2
- (b) ClOBa
- (c) H2O
- (d) BaClO3
- (e) Ba(ClO3)2
- 9.
- The precipitate formed when barium chloride is treated with sulfuric acid is _______ .
- (a) BaS2O4
- (b) BaSO3
- (c) BaSO2
- (d) BaSO4
- (e) BaS
- 10.
- The spectator ion(s) in the following reaction is/are:
Na2CO3(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq)  BaCO3(s) + 2NaNO3(aq)
BaCO3(s) + 2NaNO3(aq)
- (a) Na+ and Ba2+
- (b) Ba2+ and CO32-
- (c) CO32- and NO3-
- (d) Na+ only
- (e) Na+ and NO3-
- 11.
- Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
- (a) For the reaction of a strong acid with a strong soluble base, the net ionic equation is always
H+ + OH-  H2O
H2O
- (b) "Spectator ions" appear in the total ionic equation for a reaction, but not in the net ionic equation.
- (c) HF, HCl, and HNO3 are all examples of strong acids.
- (d) Titration is a process which can be used to determine the concentration of a solution.
- (e) In a neutralization reaction, an acid reacts with base to produce a salt and H2O.
- 12.
- What
is the net ionic equation for the acid-base reaction that occurs when
acetic acid and potassium hydroxide solutions are mixed?
- (a) H+(aq) + OH-(aq)
 H2O(l)
H2O(l)
- (b) H+(aq) + KOH(s)
 K+(aq) + H2O(l)
K+(aq) + H2O(l)
- (c) CH3COOH(aq) + KOH(s)
 KCH3COO(aq) + H2O(l)
KCH3COO(aq) + H2O(l)
- (d) CH3COO-(aq) + H+(aq) + K+(aq) + OH-(aq)
 K+(aq) + CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l)
K+(aq) + CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l)
- (e) CH3COOH(aq) + OH-(aq)
 CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l)
CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l)
- 13.
- What is the net ionic equation for the acid-base reaction that occurs when nitric acid is added to copper(II) hydroxide?
- (a) H+(aq) + OH-(aq)
 H2O(l)
H2O(l)
- (b) 2H+(aq) + Cu(OH)2(s)
 Cu2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Cu2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
- (c) 2HNO3(aq) +Cu(OH)2(s)
 Cu(NO3)2(s) + 2H2O(l)
Cu(NO3)2(s) + 2H2O(l)
- (d) 2H+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq)
 Cu(NO3)2(s) + 2H2O(l)
Cu(NO3)2(s) + 2H2O(l)
- (e) 2H+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq)
 Cu2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Cu2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + 2H2O(l)
- 14.
- Which of the following statements is FALSE given the following net ionic equation?
H3PO4(aq) + 3OH-(aq)  PO43-(aq) + 3H2O(l)
PO43-(aq) + 3H2O(l)
- (a) If all the water evaporated away, the salt remaining could possibly be Na3PO4.
- (b) The acid, H3PO4, is a weak electrolyte.
- (c) The base involved must be a strong soluble base.
- (d) This is classified as a neutralization reaction.
- (e)This could be the net ionic equation for H3PO4 reacting with Al(OH)3.
- 15.
- Which of the following statements is FALSE given the following net ionic equation?
2H+(aq) + Cu(OH)2(s)  Cu2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Cu2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
- (a) If all the water evaporated away, the salt remaining could possibly be CuS.
- (b) The acid involved must be a strong electrolyte.
- (c) The base, Cu(OH)2, is an insoluble base.
- (d) This could be the net ionic equation for HNO3 reacting with Cu(OH)2.
- (e) This is classified as a neutralization reaction.
- 16.
- Determine the oxidation number of carbon in K2CO3.
- (a) 0
- (b) +2
- (c) +4
- (d) -2
- (e) some other value
- 17.
- Which assignment of oxidation number is INCORRECT for the blinking element?
- (a) K22O7; +6
- (b) H3; +3
- (c) H2O2-; +1
- (d) O32-; +4
- (e) (NO3)2; +2
- 18.
- Consider the following reaction:
4NH3 + 5O2  4NO + 6H2O
The element being oxidized and the oxidizing agent are:
4NO + 6H2O
The element being oxidized and the oxidizing agent are:
- (a) N and NH3
- (b) N and O2
- (c) O and NH3
- (d) O and O2
- (e) H and NH3
- 19.
- Given
that the Activity Series is: Na>Mg>Cu>Ag>Au, which one of
the following answers represents the ions that would not be displaced from aqueous solution (reduced) by metallic magnesium?
- (a) Na+
- (b) Cu2+
- (c) Cu2+ and Au+
- (d) Cu2+, Ag+ and Au+
- (e) Na+, Cu2+, Ag+ and Au+
- 20.
- Which name/formula combination is WRONG?
- (a) phosphorous acid / H3PO4
- (b) nitrogen oxide / NO
- (c) acetate ion / CH3COO-
- (d) sodium chromate / Na2CrO4
- (e) calcium hypobromite / Ca(BrO)2
- 21.
- Which name/formula combination is WRONG?
- (a) chlorous acid / HClO2
- (b) dinitrogen tetroxide / N2O4
- (c) ammonium nitrate / NH4NO3
- (d) copper(II) periodate / CuIO4
- (e) potassium permanganate / KMnO4
Answers:
1. (d) 2. (d) 3. (c) 4. (a) 5. (b) 6. (a) 7. (c) 8. (e) 9. (d) 10. (e) 11. (c) 12. (e) 13. (b) 14. (e) 15. (a) 16. (c) 17. (b) 18. (b) 19. (a) 20. (a) 21. (d)

 Click here to return to the top.
Click here to return to the top.

 Choose your next chapter:
Choose your next chapter:
Fundamentals of Chemistry
| Chemical Formulas & Composition Stoichiometry
| Chemical Equations & Rxn Stoichiometry
| Types of Chemical Reactions
|
| Atomic Structure
| Chemical Periodicity
| Chemical Bonding
| Molecular Structure/Covalent Bonding Theories| Molecular Orbital Theory |
| Acids/Bases/Salts - Theory & Rxns
| Acids/Bases/Salts - Calculations (including balancing redox rxns)
| Gases
| Solids & Liquids
| Solutions |
| Thermodynamics
| Kinetics
| Equilibrium
| Aqueous Equilibrium - Acids/Bases/Salts
| Aqueous Equilibrium - Buffers & Titrations
|
| Aqueous Equilibrium - Slightly Soluble Salts
| Electrochemistry
| Metallurgy
| Metal Properties & Rxns
| Nonmetals & Metalloids
|
| Coordination Compounds
| Nuclear Chemistry
| Organic Chem - Formulas/Names/Properties
| Organic Chem - Shapes/Rxns/Biopolymers |

 To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.
To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.


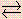 NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
 BaCO3(s) + 2NaNO3(aq)
BaCO3(s) + 2NaNO3(aq) H2O
H2O H2O(l)
H2O(l)
 K+(aq) + H2O(l)
K+(aq) + H2O(l)
 KCH3COO(aq) + H2O(l)
KCH3COO(aq) + H2O(l)
 K+(aq) + CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l)
K+(aq) + CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l)
 CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l)
CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l)
 H2O(l)
H2O(l)
 Cu2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Cu2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
 Cu(NO3)2(s) + 2H2O(l)
Cu(NO3)2(s) + 2H2O(l)
 Cu(NO3)2(s) + 2H2O(l)
Cu(NO3)2(s) + 2H2O(l)
 Cu2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Cu2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + 2H2O(l)
 PO43-(aq) + 3H2O(l)
PO43-(aq) + 3H2O(l) Cu2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Cu2+(aq) + 2H2O(l) 4NO + 6H2O
4NO + 6H2O
 Click here to return to the top.
Click here to return to the top.
 Choose your next chapter:
Choose your next chapter: 
 To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.
To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.