 | Organic Chemistry -
Formulas, Names & Properties
Examples of
Multiple Choice Questions
|
- 1.
- What makes carbon such a unique element?
- (a) Elemental carbon comes in two forms, diamond and graphite.
- (b) Carbon forms four bonds, although the ground state configuration would predict the formation of fewer bonds.
- (c) Carbon forms covalent bonds rather than ionic bonds.
- (d) To a greater extent than any other element, carbon can bond to itself to form straight chains, branched chains and rings.
- (e) Carbon has two stable isotopes, carbon-12 and carbon-13.
- 2.
- The hybridization of carbon atoms in alkanes is
- (a) sp
- (b) sp2
- (c) sp3
- (d) sp3d
- (e) sp3d2
- 3.
- A molecule with the formula C3H8 is a(n):
- (a) hexane
- (b) propane
- (c) decane
- (d) butane
- (e) ethane
- 4.
- Select the correct IUPAC name for:
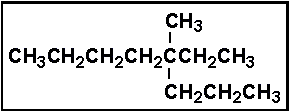
- (a) 5-methyl-5-ethyloctane
- (b) 5-methyl-5-propylheptane
- (c) 4-ethyl-4-methyloctane
- (d) 3-methyl-3-propyloctane
- (e) 3-methyl-3-propylheptane
- 5.
- Select the correct IUPAC name for:
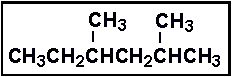
- (a) 1,1,3-trimethylpentane
- (b) 1-ethyl-1,3-dimethylbutane
- (c) 2,4-dimethylhexane
- (d) 3,5-dimethylhexane
- (e) 3,5,5-trimethylpentane
- 6.
- Select the correct IUPAC name for:
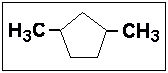
- (a) 1,4-dimethylcyclopentane
- (b) 1,3-dimethylcyclopentane
- (c) 2,5-dimethylcyclopentane
- (d) 2,3-dimethylcyclopentane
- (e) 2,4-dimethylcyclopentane
- 7.
- The general formula for noncyclic alkenes is:
- (a) CnH2n+2
- (b) CnH2n
- (c) CnH2n-2
- (d) CnHn+2
- (e) CnHn
- 8.
- The correct name for the compound given below is:
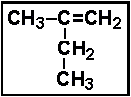
- (a) 2-methyl-1-butene
- (b) 2-ethyl-1-propene
- (c) 2-ethyl-1-pentane
- (d) 3-methyl-2-butene
- (e) pentene
- 9.
- Select the best name for:
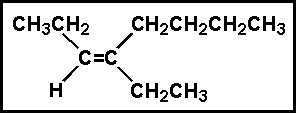
- (a) 4-ethyl-cis-3-octene
- (b) 4-ethyl-trans-3-octene
- (c) 4-butyl-cis-3-hexene
- (d) 5-ethyl-trans-5-octene
- (e) 5-ethyl-cis-5-octene
- 10.
- Name the following compound:
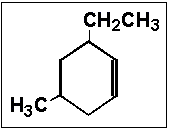
- (a) 6-ethyl-4-methylcyclohexene
- (b) 6-ethyl-3-methylcyclohexene
- (c) 3-ethyl-5-methylcyclohexene
- (d) 6-ethyl-4-methylcyclohex-1-ene
- (e) 6,4-dialkylcyclohexene
- 11.
- What is the IUPAC name of the following compound?
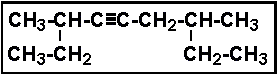
- (a) 2,6-diethyl-3-nonyne
- (b) 2,5-diethyl-3-nonyne
- (c) 3,7-dimethyl-5-nonyne
- (d) 3,7-dimethyl-4-nonyne
- (e) 2,6-diethyl-3-heptyne
- 12.
- The following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula?
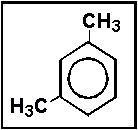
- (a) C8H10
- (b) C6H6
- (c) C6H8
- (d) C8H12
- (e) C8H6
- 13.
- How many actual double bonds does the benzene ring possess?
- (a) None, carbon-carbon bonds in benzene are delocalized around the ring
- (b) 1 double bond
- (c) 2 double bonds
- (d) 3 double bonds
- (e) 4 double bonds
- 14.
- Para-xylene is the same as:
- (a) 1,2-dimethylbenzene
- (b) 1,3-diethylbenzene
- (c) 1,3-dimethylbenzene
- (d) 1,4-diethylbenzene
- (e) 1,4-dimethylbenzene
- 15.
- Which of the following formulas represents an alkene?
- (a) CH3CH2CH3
- (b) CH3CH3
- (c) CH3CH2CHCH2
- (d) CH3CH2Cl
- (e) CHCH
- 16.
- What is the name of the following compound?
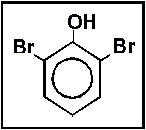
- (a) 1,3-dibromophenol
- (b) 2,5-dibromophenol
- (c) 2,6-dibromophenol
- (d) m-dibromophenol
- (e) o-dibromophenol
- 17.
- Which one of the following is a secondary alcohol?
- (a) CH3CH2OH
- (b) CH3OH
- (c) CH3CH(OH)CH3
- (d) (CH3)C3OH
- (e) none of these
- 18.
- Select the IUPAC name for: (CH3)2CHCH(OH)CH2C(CH3)3.
- (a) 2,5,5-trimethyl-3-hexanol
- (b) 1,1,4,4-pentamethylbutanol
- (c) 1,1-dimethylisopentanol
- (d) 2,5-dimethyl-4-hexanol
- (e) none of these
- 19.
- Which is NOT a physical property of alcohols or phenols?
- (a) Phenols are generally only slightly soluble in water.
- (b) The solubilities of normal primary alcohols in water decrease with increasing molecular weight.
- (c) The hydroxyl group of an alcohol is nonpolar.
- (d) Due to hydrogen bonding, boiling points of alcohols are much higher than those of corresponding alkanes.
- (e) Boiling points of normal primary alcohols increase with increasing molecular weight.
- 20.
- Give the IUPAC name of this compound: CH3OCH2CH3.
- (a) dimethyl ether
- (b) methoxyethane
- (c) methylethyloxide
- (d) propyl ether
- (e) none of the above
- 21.
- The compound below is classified as a _____ .
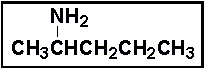
- (a) primary amine
- (b) secondary amine
- (c) tertiary amine
- (d) primary amide
- (e) secondary amide
- 22.
- The systematic name for the compound in Problem 21 is _____ .
- (a) pentyl amine
- (b) methyl-n-propyl amine
- (c) diethyl amine
- (d) 2-aminopentane
- (e) isobutylamine
- 23.
- Select the IUPAC name for the compound below.
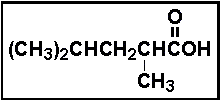
- (a) 2,4-dimethylpentanoic acid
- (b) 1,1,3-trimethylbutanoic acid
- (c) 1-hydroxy-2,4-dimethylpentanone
- (d) 2-carboxyisohexane
- (e) none of these
- 24.
- Select the best name for:
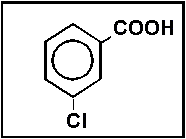
- (a) m-chlorobenzoic acid
- (b) o-chlorobenzaldehyde
- (c) p-chlorobenzoate
- (d) m-chlorosalicylic acid
- (e) none of these
- 25.
- The best classification for the following compound is: _____ .
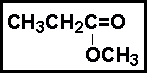
- (a) aldehyde
- (b) ester
- (c) ketone
- (d) carboxylic acid
- (e) alcohol
- 26.
- The compound given below is called _____ .
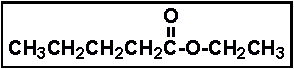
- (a) butyl acetate
- (b) ethyl pentanoate
- (c) propyl pentanoate
- (d) ethyl butanoate
- (e) butyl ethanoate
- 27.
- The compound illustrated below is called _____ .
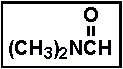
- (a) acetamide
- (b) formyl acetamide
- (c) dimethyl acetate
- (d) N,N-dimethylformamide
- (e) dimethylamine
- 28.
- The functional group given below is characteristic of organic _____ .
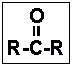
- (a) ketones
- (b) acids
- (c) aldehydes
- (d) esters
- (e) alcohols
Answers:
1. (d) 2. (c) 3. (b) 4. (c) 5. (c) 6. (b) 7. (b) 8. (a) 9. (a) 10. (c) 11. (d) 12. (a) 13. (a) 14. (e) 15. (c) 16. (c) 17. (c) 18. (a) 19. (c) 20. (b) 21. (b) 22. (d) 23. (a) 24. (a) 25. (b) 26. (b) 27. (d) 28. (a)

 Click here to return to the top.
Click here to return to the top.

 Choose your next chapter:
Choose your next chapter:
| Fundamentals of Chemistry
| Chemical Formulas & Composition Stoichiometry
| Chemical Equations & Rxn Stoichiometry
| Types of Chemical Reactions
|
| Atomic Structure
| Chemical Periodicity
| Chemical Bonding
| Molecular Structure/Covalent Bonding Theories| Molecular Orbital Theory |
| Acids/Bases/Salts - Theory & Rxns
| Acids/Bases/Salts - Calculations (including balancing redox rxns)
| Gases
| Solids & Liquids
| Solutions |
| Thermodynamics
| Kinetics
| Equilibrium
| Aqueous Equilibrium - Acids/Bases/Salts
| Aqueous Equilibrium - Buffers & Titrations
|
| Aqueous Equilibrium - Slightly Soluble Salts
| Electrochemistry
| Metallurgy
| Metal Properties & Rxns
| Nonmetals & Metalloids
|
| Coordination Compounds
| Nuclear Chemistry
| Organic Chem - Formulas/Names/Properties
| Organic Chem - Shapes/Rxns/Biopolymers |

 To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.
To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.








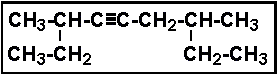





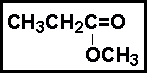


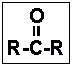

 Click here to return to the top.
Click here to return to the top.
 Choose your next chapter:
Choose your next chapter: 
 To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.
To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.