 | Liquids and Solids
Examples of
Multiple Choice Questions
|
- 1.
- What type of intermolecular forces are due to the attraction between temporary dipoles and their induced temporary dipoles?
- (a) metallic bond
- (b) London dispersion
- (c) hydrogen bond
- (d) ionic bond
- (e) covalent bond
- 2.
- What type of interparticle forces holds liquid N2 together?
- (a) ionic bonding
- (b) London forces
- (c) hydrogen bonding
- (d) dipole-dipole interaction
- (e) covalent bonding
- 3.
- Which response includes only those compounds that can exhibit hydrogen bonding?
CH4, AsH3, CH3NH2, H2Te, HF
- (a) AsH3, H2Te
- (b) AsH3, CH3NH2
- (c) CH4, AsH3, H2Te
- (d) CH3NH2, HF
- (e) HF, H2Te
- 4.
- Which of the following boils at the highest temperature?
- (a) CH4
- (b) C2H6
- (c) C3H8
- (d) C4H10
- (e) C5H12
- 5.
- Which probably has the lowest boiling point at 1.00 atm?
- (a) HF
- (b) HCl
- (c) HBr
- (d) HI
- (e) H2SO4
- 6.
- The normal boiling point of a liquid is
- (a) the temperature at which the vapor pressure equals 760 torr.
- (b) the temperature above which the substance cannot exist as a liquid regardless of the pressure.
- (c) the temperature at which the gas molecules have more kinetic energy than the molecules in the liquid.
- (d) the only temperature at which there can be equilibrium between liquid and gas.
- (e) the temperature at which the liquid will usually boil.
- 7.
- Which of the following changes would increase the vapor pressure of a liquid?
- 1. an increase in temperature
- 2. an increase in the intermolecular forces in the liquid
- 3. an increase in the size of the open vessel containing the liquid
- (a) 1 and 2 only
- (b) 1 and 3 only
- (c) 1 only
- (d) 2 only
- (e) 3 only
- 8.
- For water (m.p. 0oC, b.p. 100oC)
- Heat of fusion = 333 J/g @ 0oC
- Heat of vaporization = 2260 J/g @ 100oC
- Specific Heat (solid) = 2.09 J/goC
- Specific Heat (liquid) = 4.18 J/goC
- Specific Heat (gas) = 2.03 J/goC
- Calculate the amount of heat (in kJ) that must be absorbed to convert 108 g of ice at 0oC to water at 70oC.
- (a) 77
- (b) 68
- (c) 64
- (d) 57
- (e) 50
- 9.
- For mercury (m.p. -39oC, b.p. 357oC)
- Heat of fusion = 11.6 J/g @ -39oC
- Heat of vaporization = 292 J/g @ 357oC
- Specific Heat (solid) = 0.141 J/goC
- Specific Heat (liquid) = 0.138 J/goC
- Specific Heat (gas) = 0.104 J/goC
- Calculate the amount of heat that must be released to convert 20.0 g of mercury vapor at 387 oC to liquid mercury at 307oC (in kJ).
- (a) 61.9
- (b) 6.56
- (c) 6.04
- (d) 5.69
- (e) 5.10
- 10.
- Which of the following phase changes is(are) endothermic?
| 1. melting | 3. sublimation | 5. deposition |
| 2. vaporization | 4. condensation | 6. freezing |
- (a) 1, 2, and 3
- (b) 4, 5, and 6
- (c) 1 and 2 only
- (d) 4 and 6 only
- (e) some other combination
- 11.
- According to the phase diagram given for Compound Y, what description is correct?
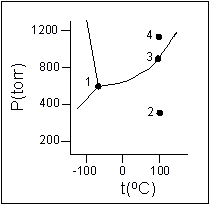
- (a) At the temperature and pressure at point 4, Y(g) will spontaneously convert to Y(l).
- (b) At 0oC and 1200 torr, Y exists as a solid.
- (c) At the pressure and temperature of point 1, Y(s) will spontaneously convert to Y(g) and no Y(l) is possible.
- (d) At the pressure and temperature at point 3, Y(s)
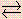 Y(g).
Y(g).
- (e) At the temperature and pressure at point 2, Y(l)
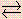 Y(g)
Y(g)
- 12.
- Where on a phase diagram can you locate conditions under which only one phase exists?
- (a) at an intersection of two lines
- (b) at the normal boiling point
- (c) at an intersection of three lines
- (d) in an area bounded by lines
- (e) at the triple point
- 13.
- In any cubic lattic, an atom lying at the corner of a unit cell is shared equally by how many unit cells?
- (a) one
- (b) two
- (c) eight
- (d) four
- (e) sixteen
- 14.
- Which statement is false?
- (a) Molecular solids generally have lower melting points than covalent solids.
- (b) Metallic solids exhibit a wide range of melting points because metallic bonds cover a wide range of bond strength.
- (c) The metallic solid can be viewed as positive ions closely packed in a sea of valence electrons.
- (d) Most molecular solids melt at lower temperatures than metallic solids.
- (e) The interactions among the molecules in molecular solids
are generally stronger than those among the particles that define
either covalent or ionic crystal lattices.
- 15.
- Which one of the following classifications is incorrect?
- (a) H2O(s), molecular solid
- (b) C4H10(s), molecular solid
- (c) KF(s), ionic solid
- (d) SiC(s), covalent solid
- (e) S(s), metallic solid
- 16.
- Which of the following compounds would be expected to have the highest melting point?
- (a) BaF2
- (b) BaCl2
- (c) BaBr2
- (d) BaI2
- (e) H2O
- 17.
- Which one of the following substances can be melted without breaking chemical bonds?
- (a) sodium sulfate
- (b) zinc chloride
- (c) sulfur dioxide
- (d) silicon dioxide
- (e) diamond
Answers:
1. (b) 2. (b) 3. (d) 4. (e) 5. (b) 6. (a) 7. (c) 8. (b) 9. (c) 10. (a) 11. (a) 12. (d) 13. (c) 14. (e) 15. (e) 16. (a) 17. (c)

 Click here to return to the top.
Click here to return to the top.

 Choose your next chapter:
Choose your next chapter:
Fundamentals of Chemistry
| Chemical Formulas & Composition Stoichiometry
| Chemical Equations & Rxn Stoichiometry
| Types of Chemical Reactions
|
| Atomic Structure
| Chemical Periodicity
| Chemical Bonding
| Molecular Structure/Covalent Bonding Theories| Molecular Orbital Theory |
| Acids/Bases/Salts - Theory & Rxns
| Acids/Bases/Salts - Calculations (including balancing redox rxns)
| Gases
| Solids & Liquids
| Solutions |
| Thermodynamics
| Kinetics
| Equilibrium
| Aqueous Equilibrium - Acids/Bases/Salts
| Aqueous Equilibrium - Buffers & Titrations
|
| Aqueous Equilibrium - Slightly Soluble Salts
| Electrochemistry
| Metallurgy
| Metal Properties & Rxns
| Nonmetals & Metalloids
|
| Coordination Compounds
| Nuclear Chemistry
| Organic Chem - Formulas/Names/Properties
| Organic Chem - Shapes/Rxns/Biopolymers |

 To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.
To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.



 Y(g).
Y(g).
 Y(g)
Y(g)

 Click here to return to the top.
Click here to return to the top.
 Choose your next chapter:
Choose your next chapter: 
 To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.
To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.