 | Coordination Compounds
Examples of
Multiple Choice Questions
|
- 1.
- The ______
sphere is enclosed in brackets in formulas for complex species, and it
includes the central metal ion plus the coordinated groups.
- (a) ligand
- (b) donor
- (c) oxidation
- (d) coordination
- (e) chelating
- 2.
- In coordination chemistry, the donor atom of a ligand is
- (a) a Lewis acid.
- (b) the counter ion
- (c) the central metal atom.
- (d) the atom in the ligand that shares an electron pair with the metal.
- (e) the atom in the ligand that accepts a share in an electron pair from the metal.
- 3.
- Consider the coordination compound, Na2[Pt(CN)4]. The Lewis acid is
- (a) [Pt(CN)4]2-
- (b) Na+
- (c) Pt
- (d) Pt2+
- (e) CN-
- 4.
- Consider the coordination compound, K2[Cu(CN)4]. A coordinate covalent bond exists between
- (a) K+ and CN-
- (b) Cu2+ and CN-
- (c) K+ and [Cu(CN)4]2-
- (d) C and N in CN-
- (e) K+ and Cu2+
- 5.
- Given the list of ligands and their corresponding names, choose the pair that disagree.
| LIGAND | NAME |
| (a) | OH- | hydroxo |
| (b) | CN- | cyanide |
| (c) | Cl- | chloro |
| (d) | H2O | aqua |
| (e) | NH3 | ammine |
- 6.
- Select the correct IUPAC name for: [FeF4(OH2)2]-
- (a) diaquatetrafluoroiron(III) ion
- (b) diaquatetrafluoroferrate(III) ion
- (c) diaquatetrafluoroiron(I) ion
- (d) diaquatetrafluoroferrate(I) ion
- (e) none of these
- 7.
- Select the correct IUPAC name for: [Co(NH3)6]2+
- (a) hexammoniacobaltate(II) ion
- (b) hexaamminecobaltate(II) ion
- (c) hexammoniacobalt(II) ion
- (d) hexaamminecobalt(II) ion
- (e) hexammoniacobalt ion
- 8.
- Which name-formula combination is NOT correct?
| FORMULA | NAME |
| (a) | [Co(NH3)4(OH2)I]SO4 | tetraammineaquaiodocobalt(III) sulfate |
| (b) | K[Cr(NH3)2Cl4] | potassium diamminetetrachlorochromate(III) |
| (c) | [Mn(CN)5]2- | pentacyanomanganate(II) ion |
| (d) | [Ni(CO)4] | tetracarbonylnickel(0) |
| (e) | Ca[PtCl4] | calcium tetrachloroplatinate(II) |
- 9.
- What is the oxidation number of the central metal atom in the coordination compound [Pt(NH3)3Cl]Cl?
- (a) -1
- (b) 0
- (c) +1
- (d) +2
- (e) +3
- 10.
- (Valance Bond Theory) Magnetic measurements indicate that [Co(OH2)6]2+ has 3 unpaired electrons. Therefore, the hybridization of the metal's orbitals in [Co(OH2)6]2+ is:
- (a) sp3
- (b) sp2d
- (c) dsp2
- (d) sp3d2
- (e) d2sp3
- 11.
- Which one of the following complexes can exhibit geometrical isomerism?
| (a) | [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] | (square planar) |
| (b) | [Zn(NH3)2Cl2] | (tetrahedral) |
| (c) | [Cu(NH3)4]2+ | (square planar) |
| (d) | [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+ | (octahedral) |
| (e) | [Cu(CN)2]- | (linear) |
- 12.
- A molecule that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image is said to exhibit which of the following?
- (a) geometrical isomerism
- (b) optical isomerism
- (c) linkage isomerism
- (d) reactive isomerism
- (e) coordination isomerism
- 13.
- In which one of the following species does the transition metal ion have d3 electronic configuration?
- (a) [Cr(NH3)6]3+
- (b) [Co(OH2)6]2+
- (c) [CoF6]3-
- (d) [Fe(CN)6]3-
- (e) [Ni(OH2)6]2+
- 14.
- (Valence Bond Theory) The coordination complex, [Cu(OH2)6]2+ has one unpaired electron. Which of the following statements are true?
- (1) The complex is octahedral.
- (2) The complex is an outer orbital complex.
- (3) The complex is d2sp3 hybridized.
- (4) The complex is diamagnetic.
- (5) The coordination number is 6.
- (a) 1, 4
- (b) 1, 2, 5
- (c) 2, 3, 5
- (d) 2, 3
- (e) 4, 5
- 15.
- (Crystal Field Theory) Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
- (a) In an octahedral crystal field, the d electrons on a metal ion occupy the eg set of orbitals before they occupy the t2g set of orbitals.
- (b) Diamagnetic metal ions cannot have an odd number of electrons.
- (c) Low spin complexes can be paramagnetic.
- (d) In high spin octahedral complexes,
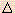 oct is less than the electron pairing energy, and is relatively very small.
oct is less than the electron pairing energy, and is relatively very small.
- (e) Low spin complexes contain strong field ligands.
- 16.
- (Crystal
Field Theory) When the valence d orbitals of the central metal ion are
split in energy in an octahedral ligand field, which orbitals are
raised least in energy?
- (a) dxy and dx2-y2
- (b) dxy, dxz and dyz
- (c) dxz and dyz
- (d) dxz, dyz and dz2
- (e) dx2-y2 and dz2
- 17.
- (Crystal Field Theory) How many unpaired electrons are there in a strong field iron(II) octahedral complex?
- (a) 0
- (b) 1
- (c) 2
- (d) 4
- (e) 6
- 18.
- (Crystal Field Theory) Consider the complex ion [Mn(OH2)6]2+ with 5 unpaired electrons. Which response includes all the following statements that are true, and no false statements?
- I. It is diamagnetic.
- II. It is a low spin complex.
- III. The metal ion is a d5 ion.
- IV. The ligands are weak field ligands.
- V. It is octahedral.
- (a) I, II
- (b) III, IV, V
- (c) I, IV
- (d) II, V
- (e) III, IV
- 19.
- (Crystal Field Theory) Consider the violet-colored compound, [Cr(OH2)6]Cl3 and the yellow compound, [Cr(NH3)6]Cl3. Which of the following statements is false?
- (a) Both chromium metal ions are paramagnetic with 3 unpaired electrons.
- (b)
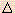 oct for [Cr(NH3)6]3+ is calculated directly from the energy of yellow light.
oct for [Cr(NH3)6]3+ is calculated directly from the energy of yellow light.
- (c)
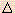 oct for [Cr(OH2)6]3+ is less than
oct for [Cr(OH2)6]3+ is less than 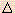 oct for [Cr(NH3)6]3+.
oct for [Cr(NH3)6]3+.
- (d) A solution of [Cr(OH2)6]Cl3 transmits light with an approximate wavelength range of 4000 - 4200 angstroms.
- (e) The two complexes absorb their complementary colors.
- 20.
- (Crystal Field Theory) Strong field ligands such as CN-:
- (a) usually produce high spin complexes and small crystal field splittings.
- (b) usually produce low spin complexes and small crystal field splittings.
- (c) usually produce low spin complexes and high crystal field splittings.
- (d) usually produce high spin complexes and high crystal field splittings.
- (e) cannot form low spin complexes.
Answers:
1. (d) 2. (d) 3. (d) 4. (b) 5. (b) 6. (b) 7. (d) 8. (c) 9. (d) 10. (d) 11. (a) 12. (b) 13. (a) 14. (b) 15. (a) 16. (b) 17. (a) 18. (b) 19. (b) 20. (c)

 Click here to return to the top.
Click here to return to the top.

 Choose your next chapter:
Choose your next chapter:
| Fundamentals of Chemistry
| Chemical Formulas & Composition Stoichiometry
| Chemical Equations & Rxn Stoichiometry
| Types of Chemical Reactions
|
| Atomic Structure
| Chemical Periodicity
| Chemical Bonding
| Molecular Structure/Covalent Bonding Theories| Molecular Orbital Theory |
| Acids/Bases/Salts - Theory & Rxns
| Acids/Bases/Salts - Calculations (including balancing redox rxns)
| Gases
| Solids & Liquids
| Solutions |
| Thermodynamics
| Kinetics
| Equilibrium
| Aqueous Equilibrium - Acids/Bases/Salts
| Aqueous Equilibrium - Buffers & Titrations
|
| Aqueous Equilibrium - Slightly Soluble Salts
| Electrochemistry
| Metallurgy
| Metal Properties & Rxns
| Nonmetals & Metalloids
|
| Coordination Compounds
| Nuclear Chemistry
| Organic Chem - Formulas/Names/Properties
| Organic Chem - Shapes/Rxns/Biopolymers |

 To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.
To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.


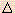 oct is less than the electron pairing energy, and is relatively very small.
oct is less than the electron pairing energy, and is relatively very small.
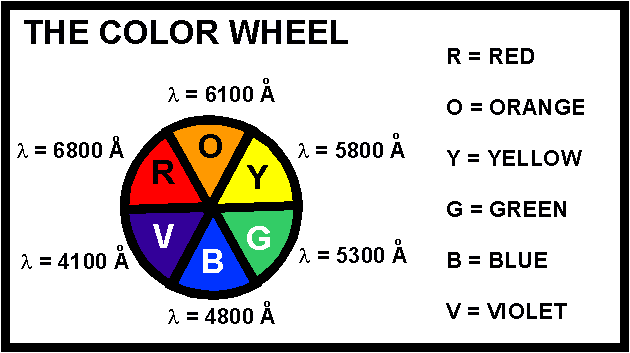
 oct for [Cr(NH3)6]3+ is calculated directly from the energy of yellow light.
oct for [Cr(NH3)6]3+ is calculated directly from the energy of yellow light.
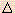 oct for [Cr(OH2)6]3+ is less than
oct for [Cr(OH2)6]3+ is less than 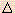 oct for [Cr(NH3)6]3+.
oct for [Cr(NH3)6]3+.

 Click here to return to the top.
Click here to return to the top.
 Choose your next chapter:
Choose your next chapter: 
 To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.
To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.