 | Sample Lab Questions Investigation #16:
"Heat Storage for Solar Heating"
|
 Click HERE for an overview of Investigation 16, compliments of Mr. Alex Redd.
Click HERE for an overview of Investigation 16, compliments of Mr. Alex Redd.
These questions have been taken from lab quizzes given in previous years.
Some of the answers are listed at the end.
- 1.
- A 50.0g block of metal, at 75.0oC is dropped into a calorimeter containing 150.0 g of water at 25.0oC. The specific heat of water is 4.18J/g
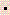 oC. If the temperature equilibrates instantaneously to 49.8oC and no heat is lost to the surroundings:
oC. If the temperature equilibrates instantaneously to 49.8oC and no heat is lost to the surroundings:
- a. (1 pt) How much heat is gained by the water?
- b. (1 pt) What is the specific heat of the metal?
- 2.
- (2 pts) If 42.8 g of H2O at 98.6oC is added to 83.7 g of H2O at 28.7oC in a perfect calorimeter (i.e. K = 0, no heat lost to surroundings), what would be the final temperature of the mixture? (Specific Heat of H2O = 4.18 J/ g
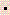 oC)
oC)
- 3.
- (3 pt) Calculate the calorimeter constant, K, using the following data:
Specific heat capacity of H2O(l) = 4.18 J/ g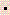 oC oC |
| Temperature of boiling water = 99.0oC |
| Mass of hot water = 100.0 g |
| Temperature of cold water = 22.3oC |
| Mass of cold water = 50.0 g |
| Temperature after instantaneous heat transfer = 44.3oC |
- 4.
- (1 pt) Why is it important in Inv. #16 that there are at least five readings with a constant rate of cooling?
- 5.
- (2 pts) In the first part of this experiment, boiling water is added to water at room temperature in the calorimeter. The heat lost by the boiling water is equal to the heat gained by what?
- 6.
- (2 pts) Describe how you determined the calorimeter constant in Inv. #16, "Heat Storage for Solar Heating."
- 7.
- (2 pts) Give two reasons why sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate would be useful as a storage agent for solar energy.
- 8.
- Define
- a. (1 pt) Specific heat capacity
- b. (1 pt) Calorimeter constant
- c. (1 pt) Seed crystal
Answers
1. (a) 1.55 x 104 J or 15.5 kJ (b) 12.3 J/goC
2. 52.3oC
3. K = 830 J/oC

 To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.
To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.


 Click HERE for an overview of Investigation 16, compliments of Mr. Alex Redd.
Click HERE for an overview of Investigation 16, compliments of Mr. Alex Redd.
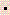 oC. If the temperature equilibrates instantaneously to 49.8oC and no heat is lost to the surroundings:
oC. If the temperature equilibrates instantaneously to 49.8oC and no heat is lost to the surroundings:
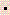 oC)
oC)
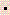 oC
oC
 To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.
To report any corrections, please e-mail Dr. Wendy Keeney-Kennicutt.